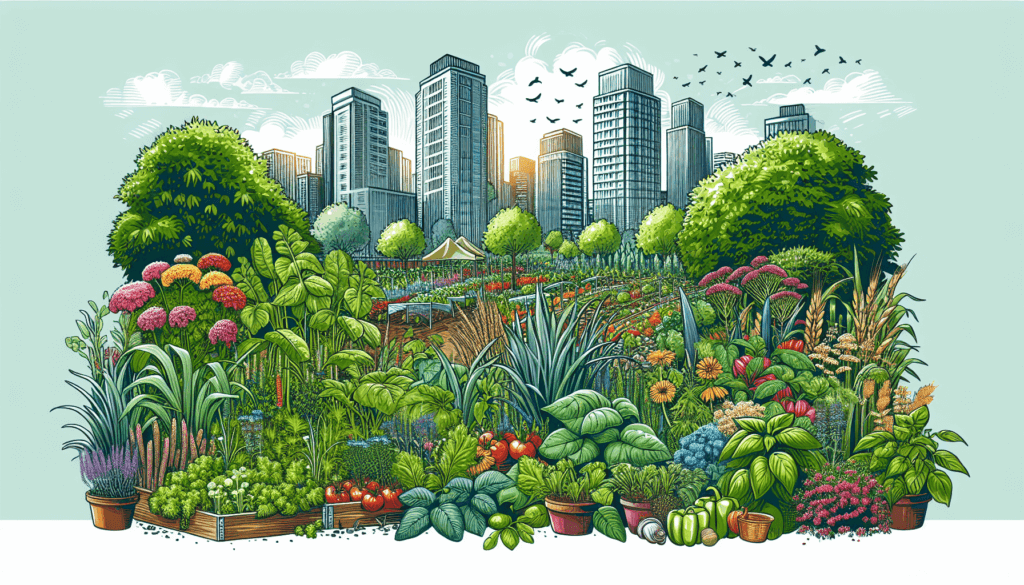
Imagine a garden where a variety of plants flourish side by side, creating a vibrant tapestry of colors, scents, and textures. This is the beauty of diverse polycultures in urban gardens. In recent years, more and more city dwellers have been embracing the concept of growing different types of plants together, and for good reason. Diverse polycultures not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban gardens but also offer numerous practical benefits, such as increased biodiversity, improved soil health, and better pest control. In this article, we will explore the many advantages of embracing diverse polycultures in urban gardens and how they contribute to a more sustainable and resilient urban environment.

Increased Biodiversity
Different plants attract a wide range of insects and animals
In an urban garden, diverse polycultures consisting of different plant species attract a wide range of insects and animals. Each plant provides a unique habitat and food source for various species. For example, flowering plants like sunflowers and lavender attract bees and butterflies, while plants with dense foliage like herbs and shrubs provide shelter for small animals. By creating a rich and varied environment, you are supporting the biodiversity of your garden and contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem.
Supports pollinators and beneficial insects
By incorporating a diverse range of plants in your urban garden, you are actively supporting pollinators and beneficial insects. Bees, butterflies, and other pollinators are essential for the reproduction of many plant species, including fruits and vegetables. By providing a variety of flowering plants with different blooming times, you can ensure a consistent food source for these pollinators throughout the year. Additionally, beneficial insects such as ladybugs and lacewings feed on pests, helping to naturally control population numbers and reduce the need for harmful pesticides.
Creates a healthier ecosystem
A diverse range of plants in your urban garden creates a healthier ecosystem overall. As mentioned earlier, different plants attract a variety of insects and animals, promoting biodiversity. This, in turn, helps to maintain a balance between different species and prevents the dominance of any one particular pest or disease. By fostering a more balanced ecosystem, you reduce the risk of outbreaks and create a healthier and more sustainable garden environment.
Reduces the risk of pests and diseases
In a diverse polyculture garden, the risk of pests and diseases is reduced. By avoiding monoculture, where a single crop dominates the garden, you prevent the buildup of pests that specifically target that crop. Instead, pests are less likely to establish themselves and spread across a diverse range of plant species. Additionally, some plants naturally repel certain pests, and the presence of these repellent plants in your garden can act as a natural barrier against infestations. By reducing the risk of pests and diseases, you can maintain the health and productivity of your urban garden.
Enhanced Soil Fertility
Various plants have different nutritional needs
Incorporating a diverse range of plant species in your urban garden benefits soil fertility. Each plant has different nutritional needs and takes up nutrients from the soil in its own unique way. By growing a variety of plants, you prevent the depletion of specific nutrients in the soil, as each plant species will utilize different nutrients. This helps to maintain a balance of essential nutrients in the soil and ensures that the soil remains fertile for future plant growth.
Cover crops prevent soil erosion
Cover crops play a vital role in enhancing soil fertility in urban gardens. These are crops that are specifically planted to cover and protect the soil. By planting cover crops like clover or winter rye, you can prevent soil erosion caused by wind or water. The roots of these crops hold the soil in place, preventing it from being washed away or blown off during heavy rains or winds. Additionally, cover crops also help to prevent weed growth, reducing the need for herbicides and minimizing competition with the main crops.
Deep-rooted plants improve soil structure
Including deep-rooted plants in your urban garden can significantly improve soil structure. Plants with deep roots, such as certain types of grasses and legumes, penetrate deeply into the soil, breaking up compacted layers and improving overall soil health. These deep roots also help to increase water infiltration and retention, preventing runoff and reducing the need for excessive watering. By improving soil structure, you create a favorable environment for plant growth and enhance the overall fertility of your urban garden.
Nitrogen-fixing plants enrich the soil with essential nutrients
Some plants, known as nitrogen-fixing plants, have the unique ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be readily used by plants. Legumes such as peas, beans, and clover are excellent examples of nitrogen-fixing plants. By including these plants in your urban garden, you can enrich the soil with essential nutrients, specifically nitrogen. This reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and promotes a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to gardening. The enriched soil contributes to healthier plant growth and higher yields in your urban garden.
Improved Harvests
Diverse polycultures maximize space and yield
Utilizing diverse polycultures in your urban garden allows you to maximize both space and yield. Unlike monoculture, where a single crop is cultivated, polycultures involve growing multiple plant species together. By carefully selecting compatible plants that have different growth habits, you can make efficient use of space. For example, taller plants like trellised tomatoes can be grown alongside shorter crops like lettuce or herbs. This intermingling of plants optimizes space utilization and increases overall yield.
Plants with different growth habits can coexist
In a diverse polyculture garden, plants with different growth habits can coexist harmoniously. Some plants grow tall and require trellising or staking, while others grow low and spreading. By strategically pairing plants with varying growth habits, you can create a garden that makes the most of vertical space while ensuring sunlight reaches all plants. This allows for efficient use of available growing space and maximizes the productivity of your urban garden.
Complementary plant relationships enhance productivity
In a diverse polyculture garden, plants can have complementary relationships that enhance overall productivity. Some plants may attract beneficial insects that prey on pests that would otherwise damage neighboring crops. Others may provide shade or act as a windbreak, protecting more delicate plants from harsh weather conditions. Companion planting, such as growing onions with carrots to repel carrot flies, is another example of how different plant species can support each other’s growth and productivity. By taking advantage of these complementary relationships, you can enhance the productivity of your urban garden.
Succession planting provides a continuous harvest
Succession planting is a key practice in urban gardening that involves planting crops at different times to ensure a continuous harvest. By staggering the planting of crops, you can extend the harvest period and avoid a glut or shortage of specific vegetables or fruits. For example, after one crop has been harvested, you can immediately plant a new crop in its place. This allows you to make full use of available growing space and maintain a steady supply of fresh produce throughout the growing season in your urban garden.
Reduced Water Usage
Different plants have varying water needs
In an urban garden, different plants have varying water needs. By incorporating a diverse range of plant species, you can better manage water usage. Some plants are more drought-tolerant and require less water, while others are more water-demanding. This diversity allows you to allocate water resources efficiently, providing the optimal amount of water to each plant species based on their specific needs. By reducing overall water usage, you contribute to water conservation efforts and promote sustainable gardening practices.
Shade from taller plants reduces evaporation
Taller plants in a diverse polyculture garden can provide shade, reducing water evaporation from the soil. As the sun’s rays are blocked or filtered, the shaded areas retain more moisture, helping to keep the soil hydrated for longer periods. This natural mechanism helps to reduce the water requirements of the plants and conserve moisture in the soil. By incorporating plants with varying heights, you can create natural shade patterns that minimize water loss due to evaporation in your urban garden.
Mulching retains moisture in the soil
Mulching is an effective technique to retain moisture in the soil and reduce water usage in an urban garden. By applying a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around your plants, you create a protective barrier that shields the soil from direct sunlight. This helps to prevent evaporation and maintain moisture levels within the soil. Mulch also acts as a weed suppressant, reducing competition for water among plants and further conserving water resources. By implementing mulching practices, you can significantly reduce water usage and promote water efficiency in your urban garden.
Diverse root systems improve water infiltration and retention
Incorporating plants with diverse root systems in your urban garden can improve water infiltration and retention in the soil. Some plants, like grasses, have fibrous shallow roots that help absorb moisture closer to the surface, preventing runoff. Others, such as deep-rooted trees or shrubs, can penetrate deeper into the soil, accessing water that is out of reach for shallow-rooted plants. This diversity of root systems enhances the water-holding capacity of the soil, reducing the need for frequent watering and promoting efficient water usage in your urban garden.

Increased Resilience
Multiple plant species can tolerate different conditions
In a diverse polyculture garden, multiple plant species provide resilience against varying environmental conditions. Different plants have different tolerances to temperature, humidity, and other factors. By incorporating a wide range of plant species, you increase the chances of having some plants that can thrive even in less favorable conditions. This resilience helps to ensure the overall stability and productivity of your urban garden, even in the face of changing weather patterns or other challenges.
Diverse polycultures are more resistant to extreme weather
Diverse polycultures in urban gardens show greater resilience and resistance to extreme weather events. Monocultures are more susceptible to damage from severe weather conditions, such as high winds or heavy rainfall. In contrast, polycultures benefit from the variety of plants and their different structural adaptations. For example, the presence of taller plants can act as a windbreak for more delicate plants, protecting them from wind damage. Similarly, the diversity of plant forms and root systems helps to mitigate the impact of heavy rainfall, reducing soil erosion and water runoff. By implementing diverse polycultures, you enhance the resilience of your urban garden against extreme weather events.
Reduces the risk of complete crop failure
A diverse polyculture garden reduces the risk of complete crop failure. When growing a single crop, the entire harvest can be wiped out by a particular pest or disease that targets that specific plant. However, in a diverse polyculture, the risk is spread across multiple plant species. Even if one crop is affected, others may remain unaffected and continue to produce a harvest. This reduces the vulnerability of your urban garden to total crop failure and ensures a reliable supply of fresh produce.
Promotes natural pest control
Diverse polycultures in urban gardens promote natural pest control. By including various plant species, you attract a diverse range of beneficial insects that prey on pests. Ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps are examples of beneficial insects that feed on garden pests like aphids or caterpillars. By providing a habitat rich in diversity, you encourage the presence and activity of these natural predators, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. This promotes a healthier and more environmentally friendly approach to pest management in your urban garden.
Improved Nutritional Value
Different plants provide a wider range of nutrients
A diverse polyculture garden in an urban setting provides a wider range of nutrients. Different plant species contain varying amounts and types of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. By incorporating a variety of vegetables, fruits, herbs, and other plants, you ensure a diverse intake of nutrients. This contributes to a more balanced and nutrient-rich diet, promoting overall health and well-being.
Combining complementary crops maximizes nutrient availability
By combining complementary crops in your urban garden, you can maximize nutrient availability. Some plant species have root systems that release beneficial nutrients into the soil, while others have higher nutrient requirements. By strategically pairing these crops, you can enhance nutrient uptake and utilization. For example, growing legumes alongside leafy greens can provide a natural source of nitrogen, promoting healthy growth in both crops. This practice of combining complementary crops optimizes nutrient availability in your urban garden and ensures maximum nutrition in your harvest.
Includes a variety of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants
A diverse polyculture garden in an urban setting offers a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Different colored fruits and vegetables contain distinct nutrients that contribute to overall health. By incorporating a diverse array of plant species in your garden, you can enjoy a variety of vitamins like vitamin C, B vitamins, and carotenoids. Additionally, mineral-rich plants like greens, beans, and nuts provide essential minerals such as iron, calcium, and magnesium. Antioxidants, which help protect against oxidative stress and chronic diseases, are also abundant in diverse polyculture gardens. By consuming a variety of plant foods, you can benefit from the multitude of nutrients they offer.
Supports a more balanced and diverse diet
A diverse polyculture garden supports a more balanced and diverse diet. By growing a wide variety of plant species, you have access to an array of fresh and nutrient-dense foods. An urban garden can supply you with fruits, vegetables, herbs, and edible flowers, allowing for a wider range of culinary options. Consuming a diverse diet ensures a balanced intake of different nutrients, leading to improved overall nutrition and supporting optimal health. Additionally, growing your own food in an urban garden promotes a connection to nature and a greater appreciation for fresh, whole foods.

Enhanced Aesthetics
Diverse polycultures create visually appealing gardens
Diverse polycultures in urban gardens create visually appealing landscapes. The combination of different plant species, each with their unique colors, textures, and forms, adds visual interest and variety to your garden. Vibrant flowers, lush foliage, and a mix of heights and shapes create an attractive and dynamic environment. Whether you choose a formal or informal garden design, the diverse range of plants creates an aesthetically pleasing space that can be enjoyed by both residents and passersby.
Combining colors, textures, and heights adds interest
By combining plants with different colors, textures, and heights, you can create an urban garden that is visually captivating. Mix bold, bright flowers with soft pastels, or combine plants with contrasting foliage to create visual impact. Consider the textures of leaves and flowers, ranging from smooth and glossy to rough and fuzzy, to add tactile interest to your garden. Varying heights through the use of trellises, tall perennials, or shrubs can provide depth and dimension to your urban garden. By paying attention to these visual elements, you can create a garden that is visually appealing and engaging.
Flowering plants attract butterflies, bees, and other pollinators
Including flowering plants in your diverse polyculture garden not only adds beauty but also attracts butterflies, bees, and other pollinators. These pollinators are vital for the reproduction of many plants, ensuring the production of fruits and seeds. By planting a variety of flowers with different blooming times, you can create a continuous source of nectar and pollen for pollinators throughout the growing season. The presence of these delightful creatures adds movement, sound, and further fascination to your urban garden.
Provides a pleasant and vibrant environment
A diverse polyculture garden in an urban setting provides a pleasant and vibrant environment. The combination of colors, textures, and growth forms creates a visually stimulating space that lifts the spirits and delights the senses. The presence of various plant species not only adds visual interest but also contributes to a healthier overall ecosystem. The abundance of life, including insects, birds, and other wildlife, creates a dynamic and thriving atmosphere, enhancing the enjoyment and tranquility of your urban garden.
Lower Maintenance
Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides
A diverse polyculture garden in an urban setting reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. The diverse range of plants promotes natural pest control, as beneficial insects become more abundant in the garden. This reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides, which can be harmful to the environment and human health. By incorporating nitrogen-fixing plants and implementing organic gardening practices, you can also minimize the use of synthetic fertilizers. This reduces the overall maintenance requirements of your urban garden and promotes a more sustainable and eco-friendly approach to gardening.
Companion planting minimizes weed growth
Companion planting is a technique used in diverse polyculture gardens to minimize weed growth and reduce maintenance. Certain plant combinations can naturally suppress weed growth by outcompeting or inhibiting their growth. For example, growing plants with dense foliage or ground-covering habits can create a natural mulch that shades out weeds, reducing the need for manual weeding or herbicides. Additionally, intercropping fast-growing crops with slower-growing ones can help shade the soil, further preventing weed establishment. By implementing companion planting strategies, you can minimize weed growth and reduce the time and effort required for maintenance in your urban garden.
Mutually beneficial plant relationships reduce labor
In a diverse polyculture garden, mutually beneficial plant relationships can reduce the labor required for maintenance. Some plants have symbiotic relationships where they mutually benefit each other’s growth or provide natural pest control. For example, growing aromatic herbs near susceptible crops can help repel pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Similarly, certain plants have deep taproots that can bring up nutrients from lower soil layers, benefiting nearby plants with shallower roots. By harnessing these mutually beneficial relationships, you can reduce the labor and interventions needed to maintain your urban garden.
Less pruning, staking, and overall care required
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban settings generally require less pruning, staking, and overall care compared to monoculture gardens. In monoculture gardens, plants often require specific pruning techniques or support structures to maintain their shape or prevent drooping. In contrast, diverse polycultures tend to have a more natural growth habit, requiring minimal pruning or staking. The variety of plants and their different growth habits allow them to support each other, reducing the need for additional maintenance efforts. This results in lower overall care requirements, making it easier to manage and enjoy your urban garden.
Community Building
Encourages community involvement in urban gardening
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas have the potential to encourage community involvement in gardening. The variety and visually appealing nature of these gardens can pique the interest and curiosity of community members. Community gardening initiatives can provide opportunities for individuals to come together, share knowledge, and actively participate in the cultivation of these gardens. By fostering a sense of ownership and pride in the community, diverse polyculture gardens can strengthen community bonds and create a shared space for residents to connect and engage with one another.
Shared knowledge and resources among gardeners
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas create opportunities for shared knowledge and resources among gardeners. By engaging in community gardening initiatives, individuals can exchange tips, techniques, and experiences with fellow gardeners. This sharing of knowledge and expertise allows for continuous learning and improvement in gardening practices. Sharing surplus produce and resources like tools or seeds further enhances the communal aspect of urban gardening, providing a sense of support and collaboration within the community.
Creates social connections and strengthens relationships
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas create social connections and strengthen relationships among community members. Gardening can be a shared activity that brings people together, fostering a sense of camaraderie and belonging. Working side by side in the garden, individuals have the opportunity to interact, share stories, and build relationships. Community gardening initiatives often organize events such as workshops, harvest festivals, or garden tours, further enhancing social interactions and creating a sense of unity within the neighborhood.
Promotes a sense of pride and ownership in the community
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas promote a sense of pride and ownership among community members. These gardens symbolize and showcase the collective efforts and achievements of the community. By actively participating in the cultivation of these gardens, individuals develop a sense of responsibility and pride in their contribution to the beauty and productivity of their community. Seeing the transformation of an empty plot into a thriving garden can instill a sense of accomplishment and generate a stronger bond between residents and their neighborhood.
Environmental Benefits
Reduces carbon footprint by minimizing transportation of food
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas reduce the carbon footprint associated with the transportation of food. Growing your own fruits, vegetables, and herbs reduces the reliance on commercially grown produce that often travels long distances. By sourcing your food locally, you contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions associated with transportation. In addition to the environmental benefits, growing your own food allows for a more direct connection to your diet and the satisfaction of knowing where your food comes from.
Absorbs CO2 and releases oxygen through photosynthesis
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas actively absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) and release oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. Plants utilize carbon dioxide during photosynthesis to produce oxygen, helping to alleviate the carbon footprint of urban environments. By creating more green spaces and incorporating a diverse range of plants, urban gardens contribute to cleaner air and the overall reduction of atmospheric CO2 levels. This process also helps to mitigate climate change by sequestering carbon and reducing the impacts of urban heat islands.
Improves air quality by filtering pollutants
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas contribute to improved air quality by filtering pollutants. Plants act as natural air purifiers, absorbing various air pollutants through their leaves and root systems. These pollutants can include volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released by common household products or pollutants emitted from vehicle exhaust. By incorporating diverse plant species in urban gardens, you can enhance air quality and reduce exposure to harmful substances, creating a healthier and more pleasant environment for both humans and wildlife.
Mitigates the urban heat island effect
Diverse polyculture gardens in urban areas help mitigate the urban heat island effect. Urban areas tend to be significantly warmer than their surrounding rural areas due to the presence of large amounts of impervious surfaces and a lack of vegetation. Urban gardens, with their diverse range of plants and increased green space, help to cool the surrounding environment through the process of transpiration and shade creation. Evapotranspiration from plants and the shading effect of trees help to reduce air temperatures, combat heat stress, and create a more comfortable urban environment. By creating green oases within cities, diverse polyculture gardens contribute to the overall cooling and well-being of urban communities.
In conclusion, the benefits of diverse polycultures in urban gardens are far-reaching and multifaceted. Increased biodiversity supports pollinators and beneficial insects, creates a healthier ecosystem, and reduces the risk of pests and diseases. Enhanced soil fertility is achieved through varied plant nutritional needs, the use of cover crops, deep-rooted plants, and nitrogen-fixing plants. Improved harvests are accomplished through maximizing space and yield, allowing plants with different growth habits to coexist, enhancing productivity through complementary plant relationships, and implementing succession planting. Reduced water usage is achieved by considering different plants’ varying water needs, utilizing shading from taller plants, employing mulching techniques, and benefiting from diverse root systems. Increased resilience is fostered through plant species’ tolerance to different conditions, resistance to extreme weather through polycultures, reduced risk of complete crop failure, and promotion of natural pest control. Improved nutritional value is attained through a wider range of nutrients, maximizing nutrient availability through complementary crops, incorporating a variety of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, and supporting a more balanced and diverse diet. Enhanced aesthetics are achieved by creating visually appealing gardens, combining colors, textures, and heights for interest, attracting butterflies and other pollinators through flowering plants, and providing a pleasant and vibrant environment. Lower maintenance is accomplished by reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, minimizing weed growth through companion planting, benefiting from mutually beneficial plant relationships, and requiring less pruning, staking, and overall care. Community building is fostered through encouraging community involvement in urban gardening, enabling shared knowledge and resources, creating social connections and strengthened relationships, and promoting a sense of pride and ownership. Finally, diverse polycultures in urban gardens contribute to various environmental benefits, including reducing the carbon footprint, absorbing CO2 and releasing oxygen, improving air quality by filtering pollutants, and mitigating the urban heat island effect. With all these benefits, it is evident that embracing diverse polycultures in urban gardens is a win-win situation for individuals, communities, and the environment.