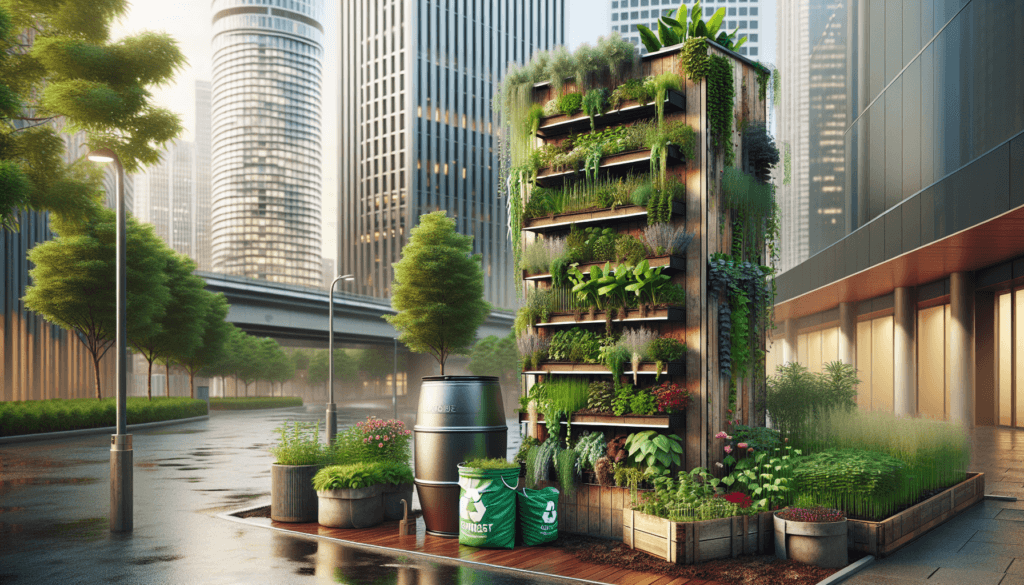
Urban gardening is becoming increasingly popular as more people seek to live a sustainable and eco-friendly lifestyle, regardless of the limited space in cities. By incorporating sustainable practices into your urban gardening routine, you can not only grow your own fresh produce but also contribute to a healthier environment. In this article, we will explore some innovative ideas and techniques that can help you cultivate a flourishing urban garden while minimizing your carbon footprint. From vertical gardening to composting, you will discover practical tips to transform your concrete jungle into a green oasis. So grab your gardening gloves and get ready to embark on a sustainable journey!

Choosing the Right Location
Understanding Sunlight Requirements
When choosing a location for your urban garden, it is important to consider the sunlight requirements of the plants you intend to grow. Some plants thrive in full sun, while others prefer partial or even full shade. Take note of the amount of direct sunlight your chosen location receives throughout the day. This information will help you select suitable plants and ensure their proper growth and development.
Considering Space Constraints
Urban gardening often comes with space constraints, but that shouldn’t discourage you. Assess the available space and think creatively about how you can maximize it. Consider vertical gardening techniques, such as trellises or hanging baskets, to utilize vertical space. Additionally, utilizing raised beds or containers can help you maximize growing area while still fitting within limited spaces, such as balconies or small yards.
Assessing Soil Quality
Soil quality is crucial for the success of any garden. Before starting your urban garden, assess the soil quality in your chosen location. Test the pH level and check for nutrient deficiencies. If the soil quality is poor, you may need to amend it with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve its fertility. Healthy soil will provide a solid foundation for your plants to grow and thrive.
Accounting for Drainage
Proper drainage is essential to prevent waterlogging, root rot, and other issues that can harm your plants. Assess the drainage capabilities of your chosen location. If the soil has poor drainage, consider using raised beds or containers with drainage holes to ensure excess water can flow out. By accounting for drainage, you can create an optimal growing environment for your urban garden.
Water Conservation
Implementing Drip Irrigation Systems
One effective way to conserve water in your urban garden is by implementing drip irrigation systems. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the roots of plants, reducing water waste through evaporation and runoff. By using this efficient method, you can ensure that water is being used where it’s needed the most, minimizing water wastage.
Harvesting Rainwater
Utilize the natural resource of rainwater by implementing rainwater harvesting techniques in your urban garden. Set up rain barrels or tanks to collect rainwater and use it for watering your plants. You can also install a simple rainwater collection system using gutters and downspouts. Harvesting rainwater not only conserves water but also reduces the strain on municipal water supplies.
Mulching to Retain Moisture
Mulching is an effective technique to retain moisture in the soil and reduce the need for frequent watering. Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around your plants. This helps to suppress weed growth, regulate soil temperature, and prevent evaporation, thus conserving water in your urban garden.
Using Native Plants
Choosing native plants for your urban garden can significantly contribute to water conservation efforts. Native plants are better adapted to the local climate and require less water compared to non-native species. They have evolved to tolerate the natural rainfall patterns of the region, reducing the need for excessive irrigation. By incorporating native plants into your garden, you can conserve water while supporting the local ecosystem.
Composting and Organic Waste Management
Creating a Compost Pile
Composting is an excellent way to manage organic waste and create nutrient-rich soil for your urban garden. Start by collecting kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials. Layer these materials in a compost bin or pile and provide a balance of green (nitrogen-rich) and brown (carbon-rich) ingredients. Turn or mix the compost regularly to promote decomposition. Over time, the compost will break down into a dark, crumbly substance that can be used to enrich your garden soil naturally.
Using Worm Bins for Vermicomposting
Worm bins, also known as vermicomposting systems, provide an efficient way to compost your organic waste. Vermicomposting involves using specific species of worms, such as red wigglers, to convert food scraps into nutrient-rich worm castings. These castings can be added to your garden soil or used as a natural fertilizer. Vermicomposting is an eco-friendly way to manage organic waste and minimize your carbon footprint.
Avoiding Chemical Fertilizers
Chemical fertilizers may provide a quick nutrient boost to your plants, but they can have negative impacts on the environment and soil health. Instead, opt for organic fertilizers and soil amendments, such as compost, bone meal, or seaweed extract. These natural alternatives not only provide nutrients but also improve soil structure and microbial activity, creating a healthier and more sustainable urban garden.
Utilizing Food Scraps
Instead of throwing away food scraps, repurpose them in your urban garden. Certain food scraps, like coffee grounds, eggshells, and fruit peels, can be used as nutrient-rich additions to your compost pile or directly added to the soil around your plants. By utilizing food scraps in this way, you can reduce waste while nourishing your garden with natural and sustainable resources.
Biocontrols and Pest Management
Attracting Beneficial Insects
Invite nature’s pest control team by attracting beneficial insects to your urban garden. Ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps are natural predators of common garden pests. Planting flowers, such as marigolds, daisies, or yarrow, can help to attract these beneficial insects. By creating a habitat that encourages their presence, you can reduce the need for chemical pesticides and maintain a balanced ecosystem in your garden.
Planting Companion Plants
Companion planting is an age-old technique in which certain plants are grown together to benefit each other. Some plants repel pests, while others attract beneficial insects or provide shade and support. For example, plant aromatic herbs like basil or rosemary near susceptible plants to repel pests or grow flowers like calendula to attract pollinators. By strategically pairing plants, you can naturally manage pest populations and promote healthy growth.
Using Natural Predators
Introduce natural predators, such as ladybugs or praying mantises, to your urban garden to control pests organically. These beneficial insects will feed on common garden pests, helping to minimize infestations without the need for harmful chemicals. Be sure to research the specific predators that target the pests you encounter in your area and release them at the appropriate times for optimal pest management.
Implementing Physical Barriers
Sometimes, physical barriers are necessary to protect your plants from pests. Use techniques like netting, row covers, or fences to keep out larger pests, such as rabbits or birds. This form of pest management is environmentally friendly and does not involve the use of chemicals. By implementing physical barriers, you can safeguard your urban garden while maintaining its sustainable practices.

Crop Rotation and Succession Planting
Maintaining Soil Health
Crop rotation is a sustainable practice that involves planting different crop types in a specific order to prevent soil depletion and reduce the risk of pests and diseases. Rotating crops helps to break pest and disease cycles and balances nutrient usage, which can result in healthier soil over time. By planning your urban garden around crop rotation, you can optimize soil health and minimize the need for chemical interventions.
Minimizing Pest and Disease Risk
Crop rotation also helps to minimize the risk of pests and diseases by disrupting the life cycles of common garden threats. Certain pests and diseases have specific plant hosts, and by rotating crops, you can avoid planting susceptible species in the same area for consecutive seasons. This reduces the likelihood of pests and diseases establishing themselves in your urban garden.
Maximizing Crop Yields and Harvests
Succession planting is a technique that involves planting new crops as soon as the previous ones are harvested. This allows you to make the most of your gardening space and extend the growing season. By continuously planting new crops throughout the year, you can maximize your harvests and enjoy fresh produce for a more extended period. Succession planting is ideal for urban gardens where space is limited but productivity is desired.
Extending the Growing Season
By implementing crop rotation and succession planting, you can extend the growing season of your urban garden. Plan your crops to take advantage of cool-season and warm-season varieties. This way, you can continue to harvest fresh vegetables and herbs throughout the year, even as the seasons change. Extending the growing season maximizes your urban garden’s productivity while making the most efficient use of your available space.
Raised Beds and Vertical Gardening
Optimizing Space Utilization
Raised beds and vertical gardening techniques are excellent ways to optimize the utilization of limited space in urban gardens. Raised beds provide a designated growing area with defined boundaries, allowing you to concentrate your plants in a smaller space. Vertical gardening, on the other hand, allows you to grow plants vertically, utilizing walls, trellises, or hanging baskets. These methods help you make the most of your available space, enabling you to grow a larger variety of plants in a compact area.
Improving Soil Drainage
Raised beds offer improved soil drainage, a critical factor in maintaining healthy plants. With raised beds, you have greater control over soil composition, ensuring that it is well-draining and suitable for the plants you are growing. By providing optimal soil drainage, raised beds help prevent waterlogging, root rot, and other issues that can harm your plants.
Reducing Weeds
Weeds can compete with your cultivated plants for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Raised beds and vertical gardening techniques can help reduce weed growth. With raised beds, you can limit contact between weed seeds in the soil and your garden. Additionally, vertical gardening minimizes ground space where weed seeds can germinate. By reducing weed growth, you can conserve resources for your desired plants and decrease the time and effort spent on weed control.
Facilitating Crop Care
Raised beds and vertical gardening methods make crop care more accessible. The elevated height of raised beds reduces the need for bending or kneeling, making it easier to tend to your plants and perform essential gardening tasks. Vertical gardening simplifies pruning, trellising, and harvesting, as the plants are within easy reach. These methods enhance the overall gardening experience and make it more convenient for urban gardeners with limited mobility or accessibility challenges.

Using Renewable and Recyclable Materials
Choosing Sustainable Containers
When selecting containers for your urban garden, opt for sustainable options. Choose containers made from renewable materials, such as bamboo or biodegradable plant-based plastics. You can also repurpose materials like old buckets or cans, reducing waste and giving them a second life. By choosing sustainable containers, you contribute to minimizing environmental impact and promote a greener approach to urban gardening.
Utilizing Reclaimed Materials
Reclaimed materials can serve multiple purposes in your urban garden. Use old wooden pallets to create raised beds or repurpose wooden crates as planters. Upcycle old bricks or concrete blocks to construct dividing walls or pathways. By utilizing reclaimed materials, you reduce waste and give new life to items that would otherwise end up in landfills.
Opting for Biodegradable Mulches
When using mulch in your urban garden, consider biodegradable options that break down naturally over time. Organic materials like straw, wood chips, or leaves make excellent mulches and improve soil fertility as they decompose. Additionally, biodegradable mulches reduce the need for synthetic materials and contribute to a more sustainable gardening practice.
Avoiding Harmful Chemicals
Many conventional gardening products contain harmful chemicals that can be detrimental to the environment, wildlife, and human health. Whenever possible, opt for organic and natural alternatives to fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. Look for products that are certified organic or utilize ingredients derived from natural sources. By avoiding harmful chemicals, you create a safer and more eco-friendly environment for your urban garden.
Promoting Biodiversity and Pollinator Habitats
Incorporating Native Plants and Wildflowers
Incorporating native plants and wildflowers into your urban garden is an excellent way to promote biodiversity and provide habitat for wildlife. Native plants are well-adapted to the local environment, making them more resilient and requiring fewer resources to thrive. Additionally, native plants attract a variety of birds, butterflies, and beneficial insects, contributing to a flourishing ecosystem within your garden.
Attracting Bees and Butterflies
Bees and butterflies play a crucial role in pollinating plants, ensuring their reproduction and fruit or seed production. Create a pollinator-friendly garden by planting flowers with abundant nectar and pollen, such as lavender, coneflowers, or milkweed. By attracting bees and butterflies, you not only support their populations but also increase the productivity of your urban garden through enhanced pollination.
Providing Shelter and Nesting Areas
Incorporate features in your urban garden that provide shelter and nesting areas for wildlife. Install birdhouses, nesting boxes, or even bee hotels to attract and support bird and insect populations. Be selective with pruning and leave some areas of undergrowth or dead vegetation to serve as habitats for small mammals, reptiles, or beneficial insects. By creating diverse microhabitats, you encourage a wider range of species to thrive in your garden.
Avoiding Pesticides Harmful to Pollinators
Certain pesticides can be harmful to pollinators, such as bees and butterflies. To promote a pollinator-friendly environment, avoid using pesticides that are toxic to these beneficial insects. Instead, focus on natural pest management techniques, such as attracting beneficial insects or using physical barriers. By avoiding harmful pesticides, you protect pollinators and contribute to the overall health of your urban garden.
Community Engagement and Education
Establishing Community Gardens
Community gardens are a wonderful way to engage with your neighbors, foster a sense of community, and promote sustainable urban gardening practices. Consider starting or joining a community garden in your area. Collaborate with other gardeners to share resources, knowledge, and the joy of growing fresh produce. Community gardens provide an opportunity for people of all ages and backgrounds to connect with nature, learn new skills, and cultivate a sense of belonging.
Organizing Workshops and Training
Organize workshops and training sessions to educate others about sustainable urban gardening practices. Share your knowledge and experience with fellow gardeners, community members, or schools. Cover topics such as composting, water conservation, pest management, and plant care techniques. By empowering others with the necessary skills and knowledge, you contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious community.
Sharing Tools and Resources
Collaborate and share gardening tools and resources with your neighbors and fellow gardeners. Consider establishing a tool-sharing program, where individuals can borrow and return gardening tools as needed. This reduces the need for every gardener to purchase their own tools, saving money and reducing the consumption of resources. Sharing tools and resources promotes a sense of unity and community, fostering a sustainable urban gardening environment.
Collaborating with Local Organizations
Collaborate with local organizations, such as environmental clubs, schools, or community centers, to promote sustainable urban gardening. Offer to host workshops, provide resources, or participate in community events related to gardening and environmental conservation. Partnering with like-minded organizations can amplify the impact of your efforts and create lasting change within your community.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Regularly Assessing Plant Health and Growth
Continuous monitoring of your plants’ health and growth is essential to identify any issues promptly. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests, diseases, or nutrient deficiencies. Monitor growth rates, leaf color, and general vitality. By staying vigilant and proactive, you can address any problems early on and ensure the overall health and productivity of your urban garden.
Analyzing Soil Composition and Nutrient Levels
Periodically analyze the soil composition and nutrient levels of your urban garden. Soil tests can provide valuable insights into the pH balance, nutrient deficiencies, or excesses that may be affecting plant health. Based on the results, you can make informed decisions about soil amendments or fertilizer application. Regular soil analysis helps maintain optimal soil health and provides a foundation for sustainable gardening practices.
Reviewing Water Usage Efficiency
Keep track of water usage in your urban garden to evaluate its efficiency. Monitor water consumption, especially during irrigation or rainfall events, and consider implementing water-saving techniques, such as drip irrigation or mulching, to optimize water use. Regularly review and adapt your watering practices to minimize waste and ensure that water is being used effectively in your garden.
Measuring Success and Adaptation
Continuously measure the success of your sustainable urban gardening practices through various metrics. Assess factors such as plant productivity, pest and disease control, resource efficiency, and community engagement. Regularly evaluate your gardening methods, taking note of what works well and what needs improvement. By monitoring and adapting your practices, you can refine your approach and achieve long-term success in your urban gardening endeavors.
In conclusion, sustainable urban gardening is not only possible but also highly rewarding. By implementing the practices outlined in this article, you can create an environmentally friendly and thriving garden in the heart of the city. From choosing the right location to continuously monitoring and evaluating your garden’s performance, each step contributes to a more sustainable and responsible approach to urban gardening. By adopting these practices and sharing your knowledge and experiences with others, you can inspire and contribute to a greener, healthier, and more vibrant community. Happy gardening!



